Restoration on Old Pension Scheme (OPS) for all Central Government Employees – Comparison of UPS, NPS and OPS: IRTSA Demand dated 18.11.2024
INDIAN RAILWAYS TECHNICAL SUPERVISORS’ ASSOCIATION
No:IRTSA/Memo-32
Date:18.11.2024
Hon’ble Minister for Finance
Government of India
Hon’ble Minister for Railways
Government of India
Respected Madam/Sir,
Sub: Restoration on Old Pension Scheme (OPS) for all Central Government Employees.
1) IRTSA brings to your kind notice on the concerns of the Central Government Employees in getting stability, dignity and financial security after their retirement which should be equal for all pensioners and family pensioners in the form of Old Pension Scheme (OPS).
2) The Unified Pension Scheme (UPS) will be implemented from 1st April 2025 and is expected to cover 23 lakh Central Government employees. Government says UPS will provide stability, dignity and financial security for government employees and their family post-retirement, ensuring their well-being and a secure future. But all these objectives of UPS will not satisfy the basic principle of “Equal Pay for Equal Work” since pension is a deferred wage.
3) In the past on many occasions, judgements of the Hon’ble Supreme Court of India strongly recommended pension payment practice. The Supreme Court held that pension is a valuable right vested on Government employees. Refusal, reduction, forfeiture of pension not allowed unless on extreme conditions.
4) 5th Pay Commission in para 127.6 of its report said that, “It needs to be averted emphatically that pension is not in the nature of alms being doled out to beggars. The senior citizens need to be treated with dignity and courtesy benefited their age. Pension is statutory, inalienable, legally enforceable right and the sweet of their brow has earned it. As such it should be fixed, revised, modified and changed in ways not entirely dissimilar to the salaries granted to Government employees”.
5) UPS assures 50% pension after completing 25 years of service, minimum pension of Rs.10,000 for 10 years of service, 60% of pension as family pension and pension, family pension & minimum pension under UPS are made inflation proof. Still there are crucial short comings of UPS compared to OPS which are listed below,
a) 50% Pension eligible on completion of 25 years, instead of 20 years in OPS. In OPS, rule 39 of CCS (Pension) Rules 2021 permits pension for Central Government employees retiring before completing 10 years of qualifying service.
b) Employees continue to contribute monthly 10% of basic pay + DA. Employee will not get return proportionate to his contribution except lump sum equal to 1/10th of last drawn monthly pay for every six months of completed service.
c) Inflation protection – Provides inflation protection by adjusting pensions based on the All-India Consumer Price Index for Industrial Workers (AICPI-IW). It is doubted that proposed DR may start from zero on 01.04.2025.
d) Commutation of pension and restoration of full pension not available in UPS.
e) Additional pension/family pension 20%, 30%, 40%, 50% and 100% after attaining the age 80, 85, 90, 95 and 100 years respectively available in OPS is not available in UPS.
f) Lump sum amount provided to employees in UPS upon superannuation, which is 1/10th of their last drawn monthly pay for every six months of completed service is very meagre compared with monthly contribution of 10% of basic pay + DA by employee.
g) If an employee takes voluntary retirement after completion of 25 years of service, he will be eligible to receive his pension only at superannuation age.
6) There are three different types of pensions ie, OPS, NPS and UPS with different benefits extended to Central Government employees working in same post discharging same duties and responsibilities. Comparison of UPS, NPS and OPS is given in annexure.
7) This is in violation of Articles 14 & 16 of constitution of India. Article-14 on Equality before law says that “the State shall not deny to any person equality before the law or the equal protection of the laws within the territory of India”. Article-16 on equality of opportunity in matters of public employment says that “there shall be equality of opportunity for all citizens in matters relating to employment or appointment to any office under the State”.
8) It is therefore requested that, all central Government employees may please be covered under OPS to maintain equality among employees and to provide stability, dignity and financial security after their retirement.
Thanking you, with regards,
Yours’ truly
K.V. RAMESH
General Secretary, IRTSA
9003149578
Copy to – For kind information & Necessary Action: Chairman & CEO, Railway Board, New Delhi-110001.
Additional Secretary, DoE, Ministry of Finance, New Delhi.
Annexure
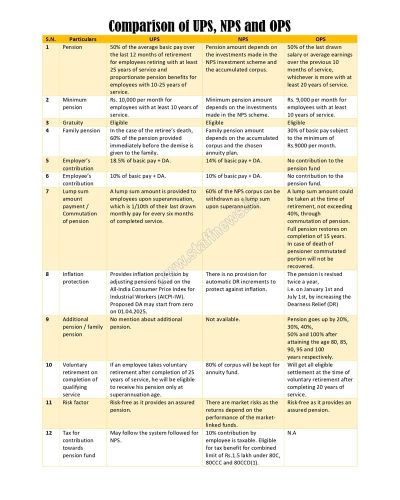
Comparison of UPS, NPS and OPS
| S.N. | Particulars | UPS | NPS | OPS |
| 1 | Pension | 50% of the average basic pay over the last 12 months of retirement for employees retiring with at least 25 years of service and proportionate pension benefits for employees with 10-25 years of service. | Pension amount depends on the investments made in the NPS investment scheme and the accumulated corpus. | 50% of the last drawn salary or average earnings over the previous 10 months of service, whichever is more with at least 20 years of service. |
| 2 | Minimum pension | Rs. 10,000 per month for employees with at least 10 years of service. | Minimum pension amount depends on the investments made in the NPS scheme. | Rs. 9,000 per month for employees with at least 10 years of service. |
| 3 | Gratuity | Eligible | Eligible | Eligible |
| 4 | Family pension | In the case of the retiree’s death, 60% of the pension provided immediately before the demise is given to the family. | Family pension amount depends on the accumulated corpus and the chosen annuity plan. | 30% of basic pay subject to the minimum of Rs.9000 per month. |
| 5 | Employer’s contribution | 18.5% of basic pay + DA. | 14% of basic pay + DA. | No contribution to the pension fund |
| 6 | Employee’s contribution | 10% of basic pay + DA. | 10% of basic pay + DA. | No contribution to the pension fund. |
| 7 | Lump sum amount payment / Commutation of pension | A lump sum amount is provided to employees upon superannuation, which is 1/10th of their last drawn monthly pay for every six months of completed service. | 60% of the NPS corpus can be withdrawn as a lump sum upon superannuation. | A lump sum amount could be taken at the time of retirement, not exceeding 40%, through commutation of pension.
Full pension restores on completion of 15 years. In case of death of pensioner commutated portion will not be recovered. |
| 8 | Inflation protection | Provides inflation protection by adjusting pensions based on the All-India Consumer Price Index for Industrial Workers (AICPI-IW).
Proposed DA may start from zero on 01.04.2025. |
There is no provision for automatic DR increments to protect against inflation. | The pension is revised twice a year,
i.e. on January 1st and July 1st, by increasing the Dearness Relief (DR) |
| 9 | Additional pension / family pension | No mention about additional pension. | Not available. | Pension goes up by 20%, 30%, 40%,
50% and 100% after attaining the age 80, 85, 90, 95 and 100 years respectively. |
| 10 | Voluntary retirement on completion of qualifying service | If an employee takes voluntary retirement after completion of 25 years of service, he will be eligible to receive his pension only at superannuation age. | 80% of corpus will be kept for annuity fund. | Will get all eligible settlement at the time of voluntary retirement after completing 20 years of service. |
| 11 | Risk factor | Risk-free as it provides an assured pension. | There are market risks as the returns depend on the performance of the market-linked funds. | Risk-free as it provides an assured pension. |
| 12 | Tax for contribution towards pension fund | May follow the system followed for NPS. | 10% contribution by employee is taxable. Eligible for tax benefit for combined limit of Rs.1.5 lakh under 80C, 80CCC and 80CCD(1). | N.A |
***
View/Download the PDF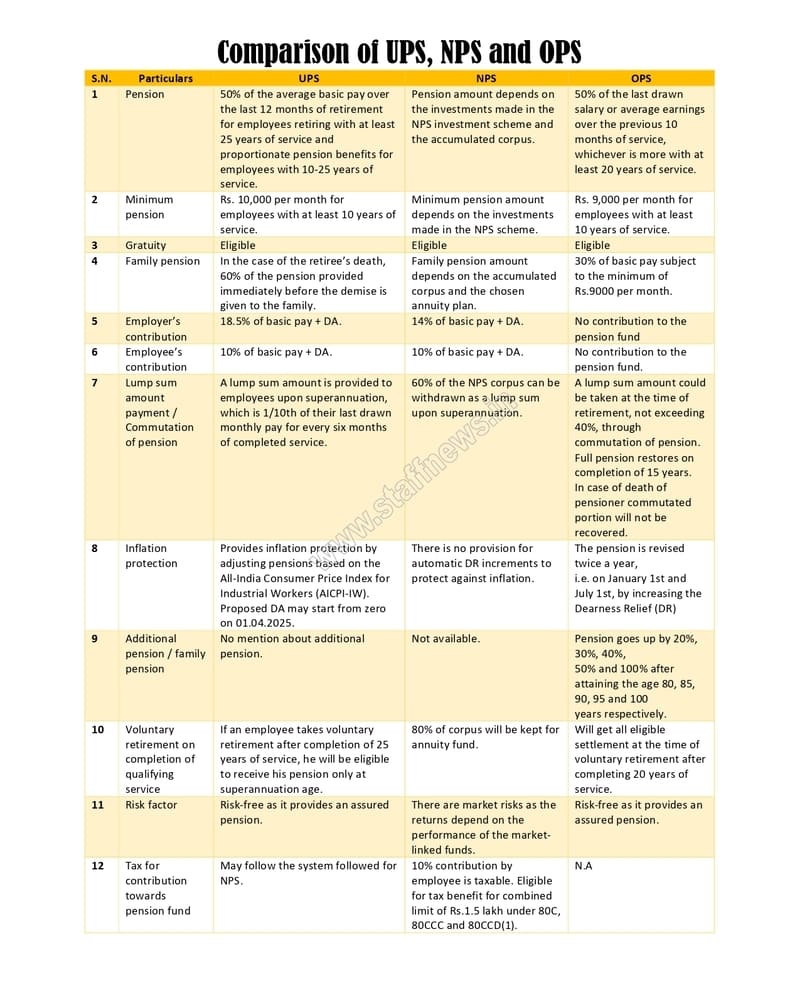
COMMENTS